Vercel provides edge runtimes which are run at locations close to the caller (client). So your serverless function is replicated to edge locations; when a user calls your endpoint, the code is executed and the response fetched from the location which is closest to your user. This minimizes the latency by canceling out the network latency due to the distance between your client and server.
Note that Vercel also has a CDN product which is called Edge Network. A CDN is a relatively old technology and most people know about it enough, in this article I will focus on edge compute products.
Vercel has two edge compute offerings which enable users to leverage the edge infrastructure. Edge middleware and edge functions:
Edge Middleware
Edge middleware intercepts the requests coming to your serverless functions. It is deployed globally on Vercel's edge locations and runs your server-side code to close to your user's origin. It runs before the request hits the edge cache. So you can update the request before being fetched from cache or processed in the serverless function. Edge Middleware runs on Vercel’s edge runtime which is a V8 Javascript engine.
Edge Functions
Edge functions are serverless functions which are executed at Vercel’s edge locations close to your user’s origin. Just like Edge Middleware, they run on edge runtime which is a V8 Javascript engine. Thanks to its runtime, it has shorter cold starts than regular serverless functions. Edge functions are run after the cache, in contrast to Edge Middleware.
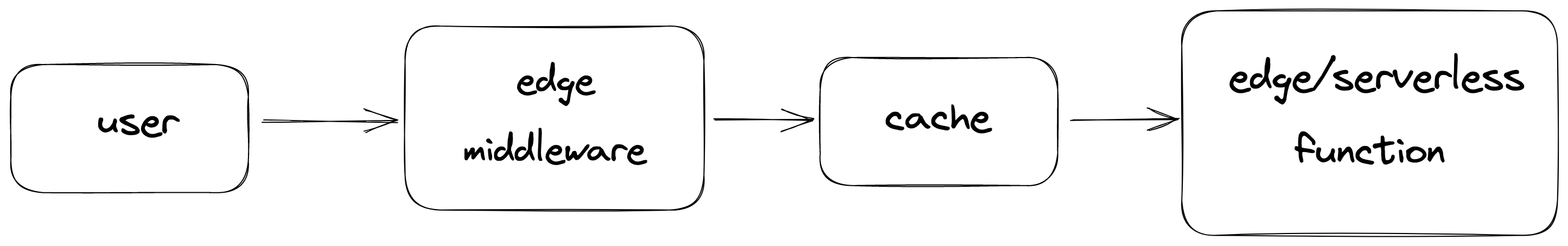
Edge Middleware vs Edge Functions
- Edge middleware runs before the backend logic while edge function is positioned to be the backend logic.
- You can use Edge functions instead of Serverless functions while you can use Edge middleware together with Serverless functions.
- Edge function is a replacement for serverless functions. Edge middleware helps you to intercept requests coming to serverless functions.
- Both run on the same infrastructure (Vercel edge) and runtime (Vercel edge runtime).
Use Cases
- Feature flags and A/B testing: You can make experiments having different versions of your content for different users or locations. Using Edge runtime, you can route your users in a faster way.
- Authentication: Instead of server-side authentication, requests can be validated at the nearest edge to the user in the edge network. Your sign-ins become faster.
- Localization: Edge runtime gives you geographical data (country, region, city) about your users. So you can restrict or update your content for different countries.
Limitations
- Native Node.js APIs are not supported (process, path, or fs).
- TCP/UDP based connections are not supported.
- Maximum size for a request is 1MB and a function is 4MB including all the code bundled.
Edge Functions vs Serverless Functions
Edge functions are cheaper and provides you low latency all over the world. Also they do not have the cold start problem so they are faster. But they have more limitations such they do not support Node API and they have more restricted code size and timeout limits.
| Serverless Function | Edge Function | |
|---|---|---|
| Maturity | GA | GA |
| Fast Start | Cold start | No cold start (faster) |
| Global low latency | No | Yes |
| Regions | Single | Edge (many) |
| Max exec time | 60s (pro) | 5s |
| Max code size | 50MB | 1MB |
| Max memory | 1024MB | 128MB |
| Price | $40 per 100GB hours | $0.65 per 1 million execution |
Recap
Vercel Edge functions and middleware are great products which broadens the capabilities of serverless functions. Canceling out the cold starts and providing low latency everywhere make them superior to single region serverless functions. But they still have some restrictions which limits them to some special use cases. It will be exciting to see how these products will evolve and if the developers will adopt them for more use cases.
Links
